In this population-based cohort study, we found that the CVST incidence rate 15 days after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination was significantly higher than the prepandemic rate. However, the higher rate of this rare adverse effect must be considered in the context of the effectiveness of the vaccine in preventing COVID-19 (absolute reduction of severe or critical COVID-19 of 940 per 100 000 PY).
Publications
An archive of industry publications, scientific journals and officially-released data.
Browse the articles related to this topic below.
Join our community on Guilded.
Published November 2020
As global conflicts take on increasingly asymmetric and “grey” forms, the ability to manipulate the human mind employing neurocognitive science techniques and tools is constantly and quickly increasing. This complements the more traditional techniques of manipulation through information technology and information warfare, making the human increasingly targeted in the cognitive warfare.
Any user of modern information technologies is a potential target. It targets the whole of a nation’s human capital.
Cognitive Warfare, June-November 2020, p. 6
Original: https://www.innovationhub-act.org/sites/default/files/2021-01/20210122_CW%20Final.pdf
“For instance, even with public criticism being high, many still perceived government approval as the yardstick for safe behaviour during COVID-19 ‘we’re allowed to do this now [so must be safe]…’. This reveals, for many, a deep set reverence for legitimate government authority, regardless of one’s personal political views.”
Net Zero: principles for successful behaviour change initiatives, p.24
This research looks at UK and OECD government-led behaviour change initiatives over the last 70 years. It identifies 9 principles that can be applied to encourage the behaviour change needed to achieve Net Zero.
The research was carried out by the Behavioural Insights Team (BIT). It was commissioned by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS).
This document has been removed from the gov.uk website. Archives can be found here:
The mortality data for England and Wales from ONS from 1 May 2021 until 17 September 2021 shows a significant excess, particularly in the 15-19 year age group. Depending on the baseline chosen, the excess for 15-19 year olds is between 16% and 47% above expected levels (see table 1 and 2). COVID-19 deaths were too small in number to account for the excess. A disproportionate number of these excess deaths were in males. A certain amount of variation by random chance would be expected but an increase of this proportion is large enough not to be dismissed without further investigation.
…Mortality has risen in younger age groups since 1st May 2021. The increase in the 15-19 year old age group is particularly noticeable, especially as deaths in this age group are uncommon. The excess deaths have a marked male predominance. An increase in ambulance call outs for patients who have had a cardiac arrest or are unconscious showed a coincidental noticeable rise from May 2021. The period also coincides with the rollout of vaccination. Finally, ONS have reported on a striking rise in age adjusted mortality rates in those with only one dose that accelerated in May 2021 to levels far exceeding those in the unvaccinated.
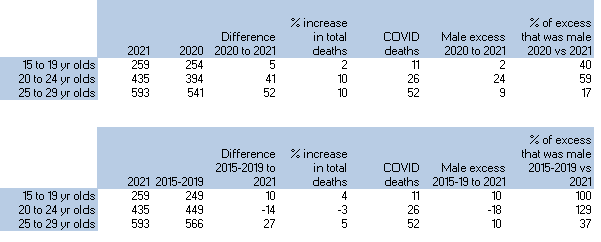
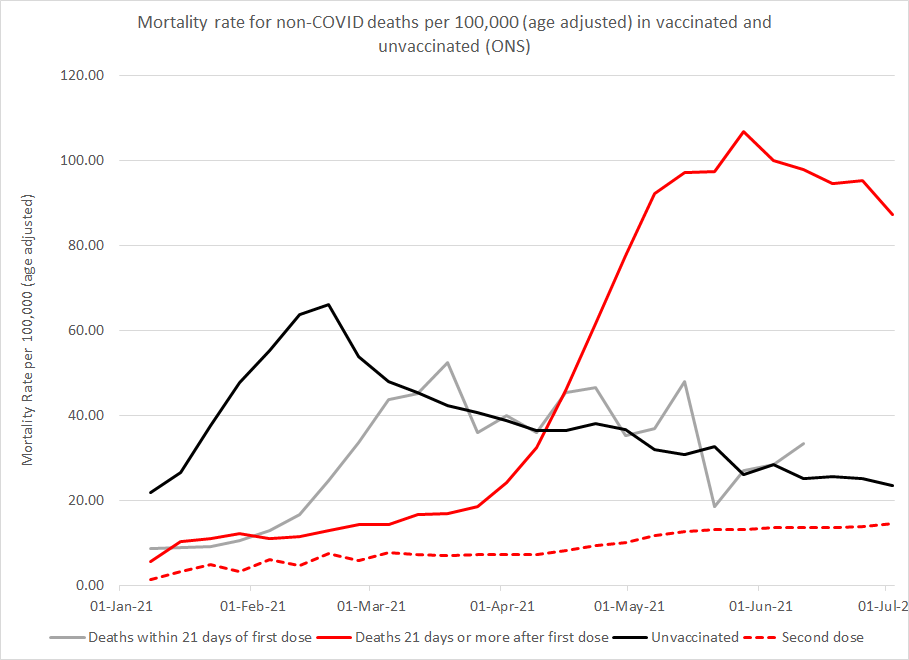
https://www.hartgroup.org/recent-deaths-in-young-people-in-england-and-wales/
Iceland on Friday suspended the Moderna anti-COVID vaccine, citing the slight increased risks of cardiac inflammation, going further than its Nordic neighbours which simply limited use of the jabs.
…This decision owed to “the increased incidence of myocarditis and pericarditis after vaccination with the Moderna vaccine, as well as with vaccination using Pfizer/BioNTech,” the chief epidemiologist said in a statement.
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-10-iceland-halts-moderna-jabs-heart-inflammation.html
This nosocomial outbreak exemplifies the high transmissibility of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant among twice vaccinated and masked individuals. This suggests some waning of immunity, albeit still providing protection for individuals without comorbidities. However, a third vaccine dose may be needed, particularly in individuals with risk factors for severe COVID-19. Appropriate use of masks, especially in high-risk settings is advised.
https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.39.2100822#html_fulltext
Conclusion
There is a substantial overlap in pathobiology between COVID-19 and WCR exposure. The evidence presented here indicates that mechanisms involved in the clinical progression of COVID-19 could also be generated, according to experimental data, by WCR exposure. Therefore, we propose a link between adverse bioeffects of WCR exposure from wireless devices and COVID-19.Specifically, evidence presented here supports a premise that WCR and, in particular, 5G, which involves densification of 4G, may have exacerbated the COVID-19 pandemic by weakening host immunity and increasing SARS-CoV-2 virulence by (1) causing morphologic changes in erythrocytes including echinocyte and rouleaux formation that may be contributing to hypercoagulation; (2) impairing microcirculation and reducing erythrocyte and hemoglobin levels exacerbating hypoxia; (3) amplifying immune dysfunction, including immunosuppression, autoimmunity, and hyperinflammation; (4) increasing cellular oxidative stress and the production of free radicals exacerbating vascular injury and organ damage; (5) increasing intracellular Ca2+ essential for viral entry, replication, and release, in addition to promoting pro-inflammatory pathways; and (6) worsening heart arrhythmias and cardiac disorders.
WCR exposure is a widespread, yet often neglected, environmental stressor that can produce a wide range of adverse bioeffects. For decades, independent research scientists worldwide have emphasized the health risks and cumulative damage caused by WCR. The evidence presented here is consistent with a large body of established research. Healthcare workers and policymakers should consider WCR a potentially toxic environmental stressor. Methods for reducing WCR exposure should be provided to all patients and the general population.
http://archive.today/2021.12.03-175456/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8580522/
The research examined data from almost 10,000 passengers on Delta’s Covid-tested flights between New York-JFK and Atlanta to Rome.
It found that a single Covid-19 molecular test performed within 72 hours of departure could decrease the rate of people actively infected on board to a level that is significantly below active community infection rates.
For example, when the average community infection rate was at 1.1% – or about one in 100 people – infection rates on Covid tested flights were 0.05% or five in 10,000 passengers.
[F]ewer than 1% of vaccine adverse events are reported. Low reporting rates preclude or slow the identification of “problem” drugs and vaccines that endanger public health. New surveillance methods for drug and vaccine adverse effects are needed. Barriers to reporting include a lack of clinician awareness, uncertainty about when and what to report, as well as the burdens of reporting: reporting is not part of clinicians’ usual workflow, takes time, and is duplicative. Proactive, spontaneous, automated adverse event reporting imbedded within EHRs and other information systems has the potential to speed the identification of problems with new drugs and more careful quantification of the risks of older drugs.
This study demonstrated that natural immunity confers longer lasting and stronger protection against infection, symptomatic disease and hospitalization caused by the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, compared to the BNT162b2 two-dose vaccine-induced immunity. Individuals who were both previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 and given a single dose of the vaccine gained additional protection against the Delta variant.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08.24.21262415v1
The majority of patients who contracted COVID-19 while in hospital did so from other patients rather than from healthcare workers, concludes a new study from researchers at the University of Cambridge and Addenbrooke’s Hospital.
The researchers analysed data from the first wave of the pandemic, between March and June 2020. While a great deal of effort is made to prevent the spread of viruses within hospital by keeping infected and non-infected individuals apart, this task is made more difficult during times when the number of infections is high. The high level of transmissibility of the virus and the potential for infected individuals to be asymptomatic both make this task particularly challenging.
Combined with other studies, these data indicate that vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals infected with the Delta variant might transmit infection. Importantly, we show that infectious SARS-CoV-2 is frequently found even in vaccinated persons when specimen Ct values are low.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.31.21261387v4.full
I reiterate our call: “slow down and get the science right—there is no legitimate reason to hurry to grant a license to a coronavirus vaccine.”
FDA should be demanding that the companies complete the two year follow-up, as originally planned (even without a placebo group, much can still be learned about safety). They should demand adequate, controlled studies using patient outcomes in the now substantial population of people who have recovered from covid. And regulators should bolster public trust by helping ensure that everyone can access the underlying data.
Background
Governments commonly fund research with specific applications in mind. Such mechanisms may facilitate ‘research translation’ but funders may employ strategies that can also undermine the integrity of both science and government. We estimated the prevalence and investigated correlates of funder efforts to suppress health behaviour intervention trial findings.
Conclusions
One in five researchers in this global sample reported being pressured to delay, alter, or not publish the findings of health behaviour intervention trials. Regulation of funder and university practices, establishing study registries, and compulsory disclosure of funding conditions in scientific journals, are needed to protect the integrity of public-good research.
GPs will get a £12.58 service fee and £10 financial supplement for each eligible 12-15 year old vaccinated.

Since the first reports of novel coronavirus in the 2020, public health organizations have advocated preventative policies to limit virus, including stay-at-home orders that closed businesses, daycares, schools, playgrounds, and limited child learning and typical activities. Fear of infection and possible employment loss has placed stress on parents; while parents who could work from home faced challenges in both working and providing full-time attentive childcare. For pregnant individuals, fear of attending prenatal visits also increased maternal stress, anxiety, and depression. Not surprising, there has been concern over how these factors, as well as missed educational opportunities and reduced interaction, stimulation, and creative play with other children might impact child neurodevelopment. Leveraging a large on-going longitudinal study of child neurodevelopment, we examined general childhood cognitive scores in 2020 and 2021 vs. the preceding decade, 2011-2019. We find that children born during the pandemic have significantly reduced verbal, motor, and overall cognitive performance compared to children born pre-pandemic. Moreover, we find that males and children in lower socioeconomic families have been most affected. Results highlight that even in the absence of direct SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 illness, the environmental changes associated COVID-19 pandemic is significantly and negatively affecting infant and child development.
Note: Commentary on this document by Dr. Naomi Wolf can be found here: FDA document admits “covid” PCR test was developed without isolated covid samples for test calibration, effectively admitting it’s testing something else
Since no quantified virus isolates of the 2019-nCoV were available for CDC use at the time the test was developed and this study conducted, assays designed for detection of the 2019-nCoV RNA were tested with characterized stocks of in vitro transcribed full length RNA (N gene; GenBank accession: MN908947.2) of known titer (RNA copies/µL) spiked into a diluent consisting of a suspension of human A549 cells and viral transport medium (VTM) to mimic clinical specimen.

This means that whilst vaccination may reduce an individual’s overall risk of becoming infected, once they are infected there is limited difference in viral load (and Ct values) between those who are vaccinated and unvaccinated. Given they have similar Ct values, this suggests limited difference in infectiousness.

The risk of severe illness and death from SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19, is extremely low in children and teenagers, according to the most comprehensive analyses of public health data, co-led by researchers at UCL.
However, Covid-19 increases the likelihood of serious illness in the most vulnerable young people, those with pre-existing medical conditions and severe disabilities, although these risks remain low overall.
The preliminary findings, published in three new pre-print studies led by UCL, the University of Bristol, University of York and the University of Liverpool, will be submitted to the UK’s Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI), the Department for Health and Social Care (DHSC)and the World Health Organisation (WHO), to inform vaccine and shielding policy for the under-18s. The studies did not look at the impact of long Covid.
Links from article:
25 CYP died of SARS-CoV-2 during the first pandemic year in England, equivalent to an infection fatality rate of 5 per 100,000 and a mortality rate of 2 per million. Most had an underlying comorbidity, particularly neurodisability and life-limiting conditions. The CYP who died were mainly >10 years and of Asian and Black ethnicity, compared to other causes of the death, but their absolute risk of death was still extremely low.