A major contributor to the mass obedience of the British people is likely to have been the activities of government-employed psychologists working as part of the “Behavioural Insights Team” (BIT). The BIT was conceived in 2010 as “the world’s first government institution dedicated to the application of behavioural science to policy”. In collaboration with governments and other stakeholders, the team aspire to use behavioural insights to “improve people’s lives and communities”. Several members of BIT, together with other psychologists, currently sit on the Scientific Pandemic Insights Group on Behaviours (SPI-B), a subgroup of SAGE, which offers advice to the government about how to maximise the impact of its Covid-19 communications.
A comprehensive account of the psychological approaches deployed by BIT is provided by an Institute of Government document titled MINDSPACE: Influencing behaviour through public policy, where it is claimed that these strategies can achieve “low cost, low pain ways of ‘nudging’ citizens … into new ways of acting by going with the grain of how we think and act”. Several interventions of this type have been woven into the Covid-19 messaging campaign, including fear (inflating perceived threat levels), shame (conflating compliance with virtue) and peer pressure (portraying non-compliers as a deviant minority) – or “affect”, “ego” and “norms”, to use the language of behavioural science.
Psychology
Browse the articles related to this topic below.
Join our community on Guilded.
The government invested in excess of £184m on communications relating to Covid-19 in 2020, figures from the Cabinet Office show.
It spent £171.9m on media activity via Manning Gottlieb OMD last year, while MullenLowe UK, which handles the majority of coronavirus advertising, was paid £12.2m.
https://www.campaignlive.co.uk/article/govt-spent-184m-covid-comms-2020/1708695
From SMITHSONIANMAG.COM, 6th March, 2017
The schools fell like dominoes across Portugal in May 2006, one after another calling upon government officials with reports of dozens, then hundreds of students struck with rashes, dizziness and difficulty breathing, just as year-end exams approached. Was it a mysterious allergic reaction, a chemical spill, a virus? After digging deeper, medical practitioners came up with a new culprit: “Strawberries With Sugar,” or in Portuguese, “Morangos com Acucar.” No, not the food—the vector for this disease was a popular teen soap opera with a saccharine title. Just before the outbreak in the real schools, a similar, life-threatening illness had plagued the teenaged characters in their fictional school.
The Portuguese students weren’t suffering from a virus or allergies: they’d come down with mass psychogenic illness.
In a psychogenic illness, a psychological trigger—rather than a biological or environmental one—causes actual physical symptoms. As sociologist Robert Bartholomew explains: “Mass hysteria is the placebo effect in reverse. People can literally make themselves ill from nothing more than an idea.” Bartholomew has studied mass hysteria extensively, and written about outbreaks around the world. “Parents and students fight the diagnosis as no one wants to accept that their kids were ‘hysterical,’” he said by email. “In reality, it’s a collective stress reaction and found in normal people.”
A new study, involving over 25,000 school-aged children, shows that masks are harming schoolchildren physically, psychologically, and behaviorally, revealing 24 distinct health issues associated with wearing masks.
The health issues and impairments observed in this study were found to affect 68% of masked children who are forced to wear a face covering for an average of 4.5 hours per day. The study also includes 17,854 health complaints submitted by parents.
Some of the health issues found in the study include: increased headaches (53%), difficulty concentrating (50%), drowsiness or fatigue (37%), malaise (42%), and nearly a third of children experience more sleep issues than they had previously and a quarter of children developed new fears.
Though these results are concerning, the study also found that 29.7% of children experienced shortness of breath, 26.4% experienced dizziness, and hundreds of the participants experiencing accelerated respiration, tightness in chest, weakness, and short-term impairment of consciousness.
A group of 47 psychologists has claimed this amounts to a strategic decision “to inflate the fear levels of the British public”, which it states is “ethically murky” and has left people too afraid to leave their homes for medical appointments. Led by former NHS consultant psychologist Dr Gary Sidley, the experts have written to the British Psychological Society (BPS) claiming the strategy is “morally questionable.”
https://www.express.co.uk/news/uk/1388315/coronavirus-feat-tactics-psychology-british-public
A phenomenon in which social trauma or anxiety combines with a suspicious event to produce psychosomatic symptoms, such as nausea, difficulty breathing, and paralysis. If many individuals come to believe that the psychosomatic outbreak is connected to the cause of the trauma or anxiety, these symptoms can spread rapidly throughout a population.
In December 2005 a mysterious illness marked by headache, fever, faintness, and numbness in extremities occurred in 13 school children in the Shelkov region of Chechnya. Many believed the illness was caused by a Russian chemical weapons attack, which precipitated the rapid spread of similar symptoms throughout the region. Medical officials determined the episode was a case of psychosomatic contagion—mass psychogenic illness—brought on by anxiety over Russian military activities in the area. There is no evidence the illnesses were caused by chemical weapons.
https://file.wikileaks.org/file/dhs-mass-psychogenic-illness-2006.pdf
Hypnotherapists have been noticing blatant hypnosis and Neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) techniques being used by the government and state-controlled media. NPL is a psychological approach that involves analyzing strategies used by successful individuals and applying them to reach a personal goal. It relates thoughts, language, and patterns of behavior learned through experience to specific outcomes.
Shutting shops at the end of October was a “psychological shock” tactic to bring home the need for restrictions to arrest the spread of the virus, the country’s health minister has admitted.
Non-essential retailers were forced to close at the end of October as infection rates reached the highest level in Europe and hospital admissions threatened to overwhelm intensive care units. Shops will reopen today after a decline in infections.
Frank Vandenbroucke told the broadcaster VRT that, with masks and social distancing, “shopping does not really involve any risk”.
Many countries across the globe utilized medical and non-medical facemasks as non-pharmaceutical intervention for reducing the transmission and infectivity of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). Although, scientific evidence supporting facemasks’ efficacy is lacking, adverse physiological, psychological and health effects are established. Is has been hypothesized that facemasks have compromised safety and efficacy profile and should be avoided from use. The current article comprehensively summarizes scientific evidences with respect to wearing facemasks in the COVID-19 era, providing prosper information for public health and decisions making.
…The data suggest that both medical and non-medical facemasks are ineffective to block human-to-human transmission of viral and infectious disease such SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, supporting against the usage of facemasks. Wearing facemasks has been demonstrated to have substantial adverse physiological and psychological effects.
A curated list of mask facts and medical publications.
COVID-19 is as politically-charged as it is infectious. Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, the WHO, the CDC and NIH’s Dr. Anthony Fauci discouraged wearing masks as not useful for non-health care workers. Now they recommend wearing cloth face coverings in public settings where other social distancing measures are hard to do (e.g., grocery stores and pharmacies). The recommendation was published without a single scientific paper or other information provided to support that cloth masks actually provide any respiratory protection. Let’s look at the data.
- Surgical masks are loose fitting. They are designed to protect the patient from the doctors’ respiratory droplets. There wearer is not protected from others’ airborne particles.
- People do not wear masks properly. Many people have the mask under the nose. The wearer does not have glasses on and the eyes are a portal of entry. If the virus lands on the conjunctiva, tears will wash it into the nasopharynx.
- Most studies cannot separate out hand hygiene.
- The designer masks and scarves offer minimal protection. They give a false sense of security to both the wearer and those around the wearer.
**Not to mention they add a perverse lightheartedness to the situation. - If you are walking alone, no need for a mask. Avoid other folks; use common sense.
- Remember: children under 2 years should not wear masks because of accidental suffocation and difficulty breathing in some.
- Even if a universal mask mandate were imposed, several studies noted that folks do not use the mask properly and over-report their wearing. Additionally, how would the mandate be enforced??
- The positive studies are models that assume universality and full compliance.
- If wearing a mask makes people go out and get Vitamin D – go for it. In the 1918 flu pandemic people who went outside did better. Early reports are showing people with COVID-19 with low Vitamin D do worse than those with normal levels. Perhaps that is why shut-ins do so poorly.
Live NHS Special – Unlocked
We get to grips with the unintended consequences of lockdown on the NHS & the health of the nation.
Martin Daubney interviews Ex-director of the WHO Cancer Programme Professor Karol Sikora.
Consultant Neurologist and MS specialist Dr Waqar Rashid
Dr Ellie Cannon NHS GP and Mail on Sunday Columnist
Dr Tom Jefferson Clinical Epidomilogist- University of Oxford’s Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
Dr John Lee Former Clinical Professor of Pathology at Hull York Medical School and Consultant Histopathologist at Rotherham General Hospital & Director of Cancer Services at Rotherham NHS Foundation Trust.
Face masks make you stupid – The Critic
Face masks make you suggestible; they make you more likely to follow someone else’s direction and do things you wouldn’t otherwise do
In Joost Meerloo’s analysis of false confessions and totalitarian regimes, The Rape of the Mind, he coins a phrase for the ‘dumbing down’ of critical resistance – menticide. “In the totalitarian regime,” he wrote, “the doubting, inquisitive, and imaginative mind has to be suppressed. The totalitarian slave is only allowed to memorise, to salivate when the bell rings.”
…The fact that masks likely don’t even work brings us to the final reason that wearing one inculcates stupidity and compliance: through a bombardment of lies, contradictions, and confusion, the state overwhelms your ability to reason clearly…
…As Theodore Dalrymple wrote, “In my study of communist societies, I came to the conclusion that the purpose of communist propaganda was not to persuade or convince, not to inform, but to humiliate; and therefore, the less it corresponded to reality the better. When people are forced to remain silent when they are being told the most obvious lies, or even worse when they are forced to repeat the lies themselves, they lose once and for all their sense of probity. To assent to obvious lies is in some small way to become evil oneself. One’s standing to resist anything is thus eroded, and even destroyed. A society of emasculated liars is easy to control.”
For a commentary on this trial, please see the video embedded below.
This study tests different messages about vaccinating against COVID-19 once the vaccine becomes available. Participants are randomized to 1 of 12 arms, with one control arm and one baseline arm. We will compare the reported willingness to get a COVID-19 vaccine at 3 and 6 months of it becoming available between the 10 intervention arms to the 2 control arms.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04460703
Commentary by Dave Cullen.
We investigate the consequences and predictors of emitting signals of victimhood and virtue. In our first three studies, we show that the virtuous victim signal can facilitate nonreciprocal resource transfer from others to the signaler. Next, we develop and validate a victim signaling scale that we combine with an established measure of virtue signaling to operationalize the virtuous victim construct. We show that individuals with Dark Triad traits-Machiavellianism, Narcissism, Psychopathy-more frequently signal virtuous victimhood, controlling for demographic and socioeconomic variables that are commonly associated with victimization in Western societies. In Study 5, we show that a specific dimension of Machiavellianism-amoral manipulation-and a form of narcissism that reflects a person’s belief in their superior prosociality predict more frequent virtuous victim signaling. Studies 3, 4, and 6 test our hypothesis that the frequency of emitting virtuous victim signal predicts a person’s willingness to engage in and endorse ethically questionable behaviors, such as lying to earn a bonus, intention to purchase counterfeit products and moral judgments of counterfeiters, and making exaggerated claims about being harmed in an organizational context. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2021 APA, all rights reserved).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32614222/
https://gwern.net/doc/psychology/personality/psychopathy/2020-ok.pdf
COVID-19 started registering with most of the British public around late February and early March. Many were concerned but not particularly afraid. Only weeks later people were terrified to leave their homes or go near other human beings. How did such a dramatic shift in public perception happen so quickly?
In early March 2020, The Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE) produced a document for the UK Government highlighting methods for rolling out new social distancing rules. There seemed to be some doubt as to whether the public would comply with the upcoming measures so SAGE outlined a methodology based on known psychological behavioural modification techniques.
SAGE, SPI-B and applied psychology
SAGE is an advisory group to the UK government responsible for making sure decision makers have access to scientific advice. We are told that the advice provided by SAGE does not represent official government policy.
SAGE also relies on expert sub-groups for COVID-19 specific advice. These sub-groups include:
- NERVTAG: New and Emerging Respiratory Virus Threats Advisory Group
- SPI-M: Scientific Pandemic Influenza Group on Modelling
- SPI-B: Independent Scientific Pandemic Influenza Group on Behaviours
The identity of individual committee members themselves were initially kept secret, purportedly due to national security. Some names were eventually released, largely due to efforts by UK businessman Simon Dolan and his legal challenge campaign. Nevertheless, two members remain anonymous.
Psychological techniques for behavioural change
The document itself, titled Options for increasing adherence to social distancing measures, was drafted by SPI-B, the behavioural science sub-group for SAGE.
SPI-B highlighted nine broad ways of achieving behavioural change in the public:
- Education
- Persuasion
- Incentivisation
- Coercion
- Enablement
- Training
- Restriction
- Environmental restructuring
- Modelling
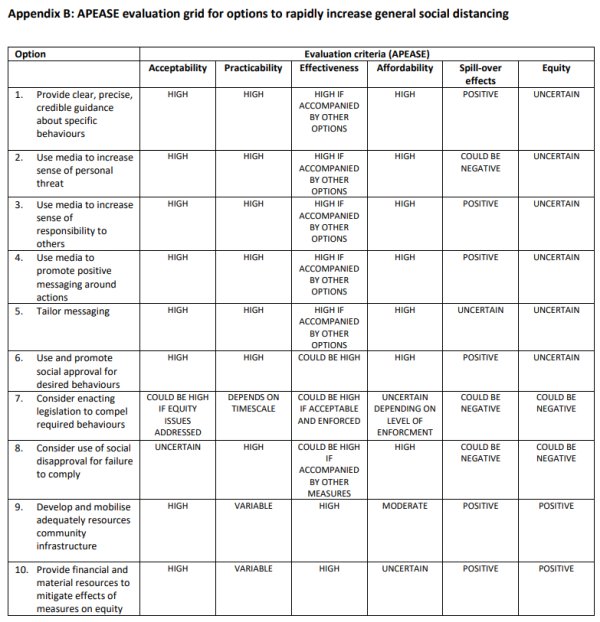
In the document, SPI-B focused on the methods most relevant to their stated goals and set out ten options that were evaluated on six criteria.
The six criteria, under the acronym APEASE, were:
- Acceptability
- Practicability
- Effectiveness
- Affordability
- Spill-over effects
- Equity
Government persuasion through fear
A key part of SPI-B’s behavioural change strategy that seems to have been adopted was to ‘persuade through fear.’ The Persuasion section of the document states:
A substantial number of people still do not feel sufficiently personally threatened.
Clearly, the psychologists felt that, as of late March, the public was still not afraid of COVID-19. It therefore suggested that the government increase the level of fear:
The perceived level of personal threat needs to be increased among those who are complacent, using hard-hitting emotional messaging.
Appendix B of the document lists ten options that can be used to increase social distancing in the public. Option 2 advises:
Use media to increase sense of personal threat.
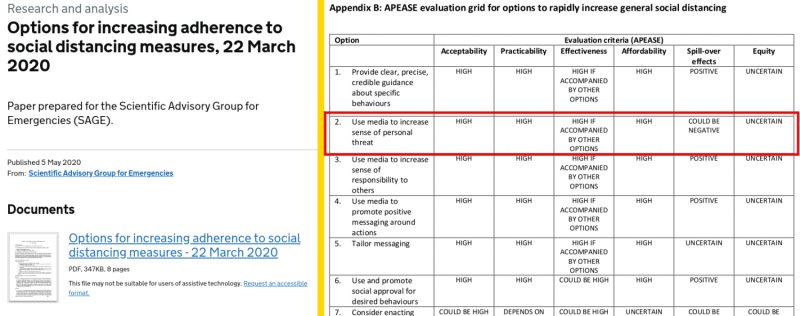
In hindsight, this explains the tone of government sponsored social media and physical billboard advertising campaigns that started appearing around April.
SPI-B recommendations to increase personal threat and use hard-hitting emotional messaging are on display with eerie imagery coupled with taglines such as:
- “Anyone can get it. Anyone can spread it.“
- “Don’t put your friends and family in danger.“
- “Stay home for your family. Don’t put their lives in danger.“
- “If you go out, you can spread it. People will die.“


Hysterical news headlines
During the first week of April 2020, the InProportion2 project noticed a change in the BBC headlines and posted the article, BBC: Informing or scaring?

The article compared hysterical BBC news headline from the first week of April 2020 with those from 2018, when mortality rates were peaking due to a bad flu season. It found no references to flu or excess mortality on the BBC home page during the 2018 peak. InProportion2 asked, “Do the headlines reflect the gravity of the situations in an equivalent way – or is additional fear being stirred up in 2020?“
Persuasion through shame and approval: Covidiots and heroes
SPI-B psychologists knew that fear on its own would not persuade everyone. Messaging needed to be tailored to take into account different ‘motivational levers.’
Some people will be more persuaded by appeals to play by the rules, some by duty to the community, and some to personal risk.
It therefore suggested using both social approval and disapproval, with compulsion (legislation) as a backup:
- Option 6: Use and promote social approval for desired behaviours
- Option 7: Consider enacting legislation to compel required behaviours
- Option 8: Consider use of social disapproval for failure to comply
We can see the obvious approval-disapproval dialectic with the ‘Heroes and Covidiots’ narrative that soon began to surface in the news. The term ‘Covidiot’ appeared around March with The Economist’s 1843 Magazine describing covidiots in this way:
Even in a pandemic, many of us are prone to judge others and find them wanting: the term “covidiot” describes any and every person behaving stupidly or irresponsibly as the epidemic spreads. Sometime in early March the word was born, and, almost as fast as the virus spread, so did instances of covidiotic behaviour.
Although it’s not clear how the term came about, it was quickly adopted in UK mainstream and social media. At the same time, we began seeing praise for heroes who ‘did the right thing’ by complying with the government measures.
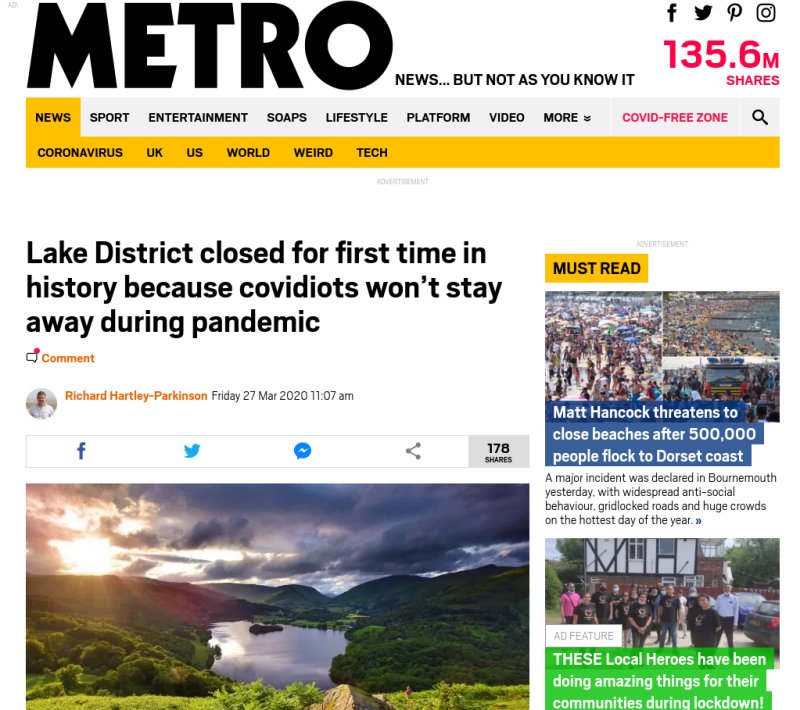
The METRO article below shows all three options in play:
- Social approval: “These local heroes have been doing amazing things…”
- Social disapproval: “Lake District closed…because covidiots won’t stay away…”
- Compulsion: “Matt Hancock threatens to close beaches…”
An incentivised media
These psychological techniques would have been impossible to deploy on the public without a compliant media. How did the government convince the media to go along with the plan?
Increased UK government media spending
Digiday, a media and marketing industry publication, reported in April that the government is becoming UK news publishers’ most important client. In the 20 April 2020 article for Digiday, Lara O’Reilly wrote:
…the government is spending more than usual, judging by their bookings. The publishers also pointed out that the lack of activity from other advertisers in the current market means the government campaigns will have an outweighed share of voice compared with normal times.

During that period, the British public started seeing coverage across media outlets with the unified “In this together” messaging. O’Reilly pointed out that the campaign was worth £35 million over a three month period.
Last week, the government and newspaper industry launched a three-month advertising partnership dubbed “All in, all together.” The campaign — worth approximately £35 million ($44 million) for the full course, according to sources — kicked off on Apr. 17, with all the U.K.’s national and regional daily news brands running near-identical cover wraps and homepage takeovers, which carried the copy, “Stay at home for the NHS, your family, your neighbours, your nation the world and life itself.”
So, we ask again: how did the government convince the media to go along with the plan? The answer is simple and obvious: with lots of money.
Psychological techniques to change behaviour
We can see that the UK Government has a public document outlining psychological techniques to change the behaviour of the population. We see a unified mass-media campaign that falls in line with these techniques. We then see a dramatic shift in public perception and behaviour.
What else can we call this but ‘brainwashing’?
Despite the open nature of what has transpired, it seems to have gained little coverage in the media. This is of no surprise since it was clearly complicit in spreading fear in the public.
Download the document
The document is freely downloadable on the gov.uk website in a page titled, “Research and analysis – Options for increasing adherence to social distancing measures, 22 March 2020“.
We encourage you to read the document, compare it with your observations about how the government and media has acted, then make up your own mind.
Updates
March 2023:
Leaked messages revealed by The Telegraph proved that Matt Hancock and other UK government ministers planned to “frighten the pants off” the public and ensure they complied with lockdown.
January 2021:
After seven months the mainstream media finally catches up. On 24th January 2021, The Express published the following article: Government accused of using Covid fear tactics to inflate anxiety levels of British public.
March 2021:
- Campaign, the world’s leading business media brand for the marketing and advertising, reported that the UK government spent more than £184m on Covid communications in 2020.
- It has emerged that German politicians, scientists and public health bureaucrats have also collaborated to induce panic to justify the first German lockdown. The source material is in German but a Twitter thread explaining the leaks in English has been archived. We will update here if an English source becomes available.
- On 18 March, the UK Government put out a tender for a £2m COVID Public Information Campaign for Northern Ireland. It is to last to years starting 1 April 2021.
- In an article for the Critic, A year of fear, Dr. Gary Sidley wrote about the role of SPI-B and The Behavioural Insights Team in bombarding the British public with fear-inducing information. Dr. Sidley is a member of the Health Advisory and Recovery Team.
April 2021:
- The mainstream media is now acknowledging the government’s psychological strategies to manipulate behaviour of the British public. On 2 April, The Telegraph published the article, State of fear: how ministers ‘used covert tactics’ to keep scared public at home.
- The UK Cabinet Office awarded £320,000,000 for COVID 19 – Media Buying Services in advertising, radio and television. The contract runs between 1st April 2021 to 31 March 2022. See our archive of UK Government COVID-19 media buying.
May 2021:
- Researcher Ian Davis reports about the ties between the UK Government and Omnicom, the New York-based corporate communications company the behind the phrases “flatten the curve”, “stay home, protect the NHS, save lives”, “rule of six” and “look into my eyes” campaigns. The UK Government has awarded Omnicom with £1.6 billion in media buy-in contracts since 2018.
- On 14th May 2020, The Telegraph published an article of SPI-B members admitting that the Use of fear to control behaviour in Covid crisis was ‘totalitarian’.
- Author, journalist, photographer and filmmaker Laura Dodsworth released her new book, A State of Fear: how the UK government weaponised fear during the Covid-19 pandemic, on 17th May 2021.
A State of Fear:
Laura Dodsworth talks about her book State of Fear on The James Delingpole Channel.
Update 27 June 2020: For a more in-depth commentary, please read How SAGE and the UK media created fear in the British public
In early March 2020, The Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies (SAGE) produced a document for the UK Government highlighting recommendations for increasing adherence to social distancing measures. There seemed to be some doubt as to whether the public would comply with the upcoming measures so SAGE developed a methodology based on criteria called ‘APEASE’.
The document itself was drafted by SPI-B, the behavioural science sub-group for SAGE. More information about SPI-B can be found in this document.

APEASE criteria
In the document, behavioural change options were set in a grid and evaluated based on the six criteria. See Appendix B in the linked document.
SPI-B’s APEASE criteria are:
- Acceptability
- Practicability
- Effectiveness
- Affordability
- Spill-over effects
- Equity
Persuasion through fear
It seems that a big part of SPI-B’s behavioural change strategy was to ‘persuade through fear.’ The Persuasion section of the document states:
The perceived level of personal threat needs to be increased among those who are complacent, using hard-hitting emotional messaging. To be effective this must also empower people by making clear the actions they can take to reduce the threat.
Appendix B of the document lists ten options that can be used to increase social distancing in the public. Option 2 advises: “Use media to increase sense of personal threat.“
Psychological techniques to change behaviour
In this document, the UK Government has openly admitted to using psychological techniques to change the behaviour of the British population. Despite the open nature of this admission, it seems to have gained little coverage in the media.
This is of no surprise since the British media was clearly complicit in spreading fear in the public.
Download the document
The document is freely downloadable on the gov.uk website in a page titled, “Research and analysis – Options for increasing adherence to social distancing measures, 22 March 2020“.
Boris Johnson has ‘trashed’ public trust and adherence to lockdown, Government advisers warned last night.
* Stephen Reicher, psychology professor at The University of St Andrew
* Susan Michie, professor of health psychology at University College London
* Professor West, health psychology professor at UCL
A confirmation that The UK Government is using psychological techniques to attack the minds of the British people.
For commentary, see:
Source document:
Despite decades of research, consensus regarding the dynamics of fear appeals remains elusive. A meta-analysis was conducted that was designed to resolve this controversy. Publications that were included in previous meta-analyses were re-analysed, and a number of additional publications were located. The inclusion criteria were full factorial orthogonal manipulations of threat and efficacy, and measurement of behaviour as an outcome. Fixed and random effects models were used to compute mean effect size estimates. Meta-analysis of the six studies that satisfied the inclusion criteria clearly showed a significant interaction between threat and efficacy, such that threat only had an effect under high efficacy (d = 0.31), and efficacy only had an effect under high threat (d = 0.71). Inconsistency in results regarding the effectiveness of threatening communication can likely be attributed to flawed methodology. Proper tests of fear appeal theory yielded the theoretically hypothesised interaction effect. Threatening communication should exclusively be used when pilot studies indicate that an intervention successfully enhances efficacy.
